TRIUMPH (12-WEEK)
TYVASO provided significant improvements in 6MWD1-3
TRIUMPH Study Design: A 12-week, placebo-controlled, multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial of TYVASO or placebo added to an ERA (bosentan) or a PDE-5i (sildenafil) in 235 clinically stable patients who were NYHA FC III (98%) or IV (2%) at baseline.2,3
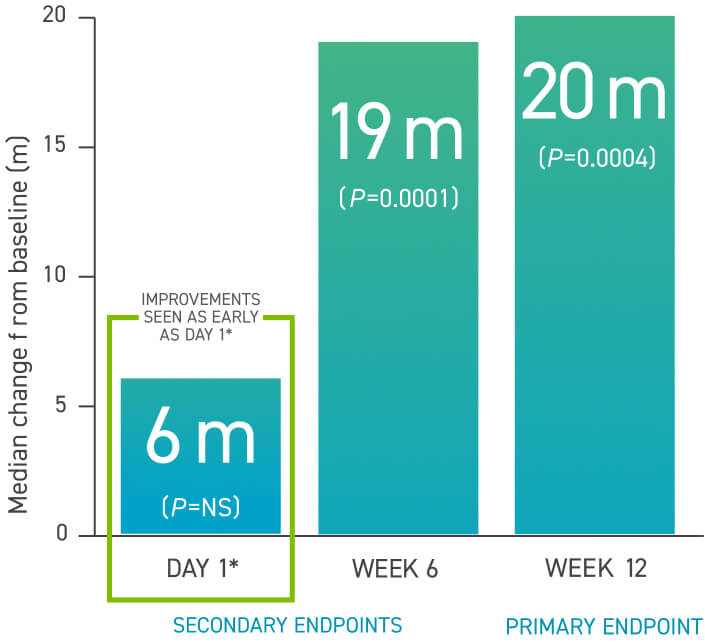
Hodges–Lehmann median difference between TYVASO treatment and placebo groups.
In Hodges-Lehmann methodology, imputed walk distance of 0 m was assigned for death, clinical worsening event, and too ill to perform 6MWT. The last observation was carried forward for all other reasons.3
>50 m
31% of patients increased 6WMD by >50 m with TYVASO compared with 12% receiving placebo1,3
Secondary endpoints
There was a significant improvement in trough 6MWD at week 12 of 14 m (P=0.0066). Compared with placebo, there was no change in Borg dyspnea score, NYHA FC, clinical worsening, or signs and symptoms of PAH from baseline.3
Patients taking TYVASO had a better quality of life score at week 12 as assessed by the MLWHF questionnaire. This included an H–L median difference of -4 in the global score (P=0.027) and -2 in the physical score (P=0.037)3*
*6MWD was measured at peak exposure (10-60 minutes after dosing) and trough exposure (≥4 hours after dosing) at week 12.2
6MWD=6-minute walk distance; 6MWT=6-minute walk test; ERA=endothelin receptor antagonist; IV=intravenous; PDE-5i=phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor; QOL=quality of life.
†Negative Hodges–Lehmann median differences in the MLWHF are considered favorable.
Ancillary assessment
TYVASO treatment resulted in a reduction of NT-proBNP levels at week 12, with an H–L between-treatment median difference in change from baseline of -187 pg/mL (95% CI: -333 to -64, P=0.0014)3
Post hoc analysis of risk status
A post hoc analysis was conducted to investigate the impact of TYVASO on risk stratification. Using REVEAL 2.0, the baseline risk status of the TRIUMPH subgroup was 35% of patients were low risk, 31% of patients were intermediate risk, and 35% of patients were high risk.4
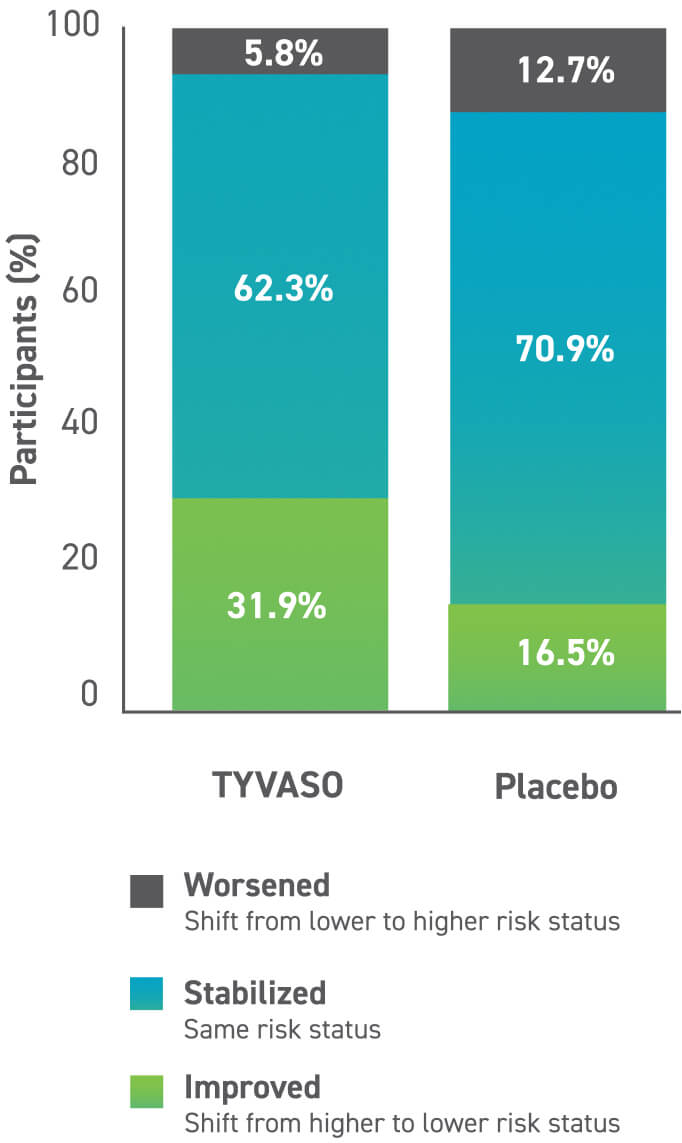
Adapted from Tonelli AR, et al. Pulm Circ. 2020;10(4):2045894020977025
32%
of patients improved their risk status4

Risk status data should be interpreted cautiously due to the limitations of post hoc analysis.
Safety
The most common adverse events with TYVASO2
TRIUMPH Study: Adverse events in ≥4% of PAH patients receiving TYVASO and more frequent than placebo.2,3
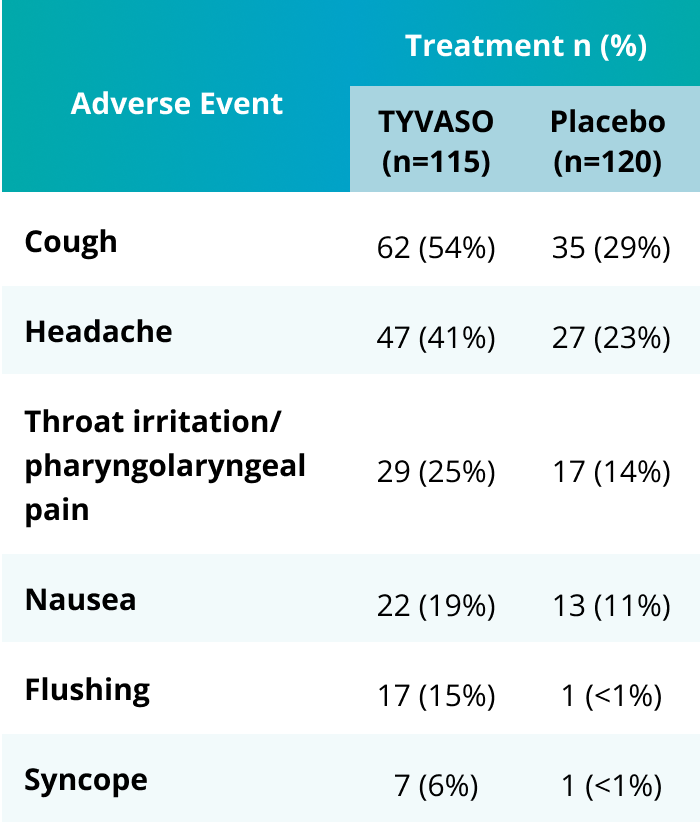
- Of the 23 total discontinuations, 7 patients from the TYVASO group discontinued due to adverse events compared with 4 from the placebo group3
- In addition, AEs occurring in ≥10% of patients were dizziness and diarrhea3
See the long-term efficacy and safety results from the TRIUMPH OLE study.
LEARN ABOUT THE EXTENSION STUDY

